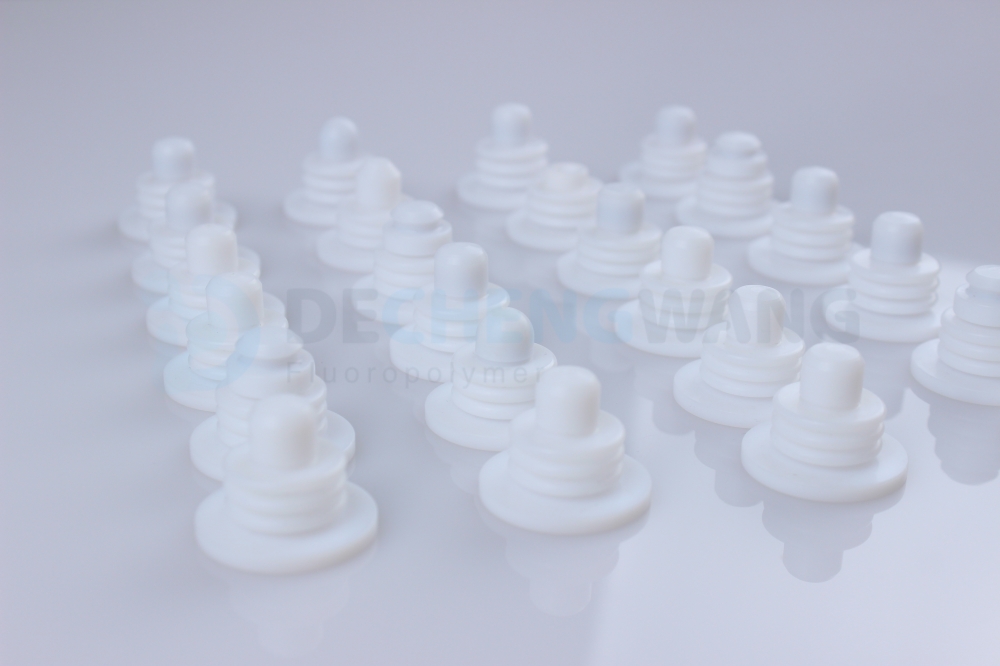
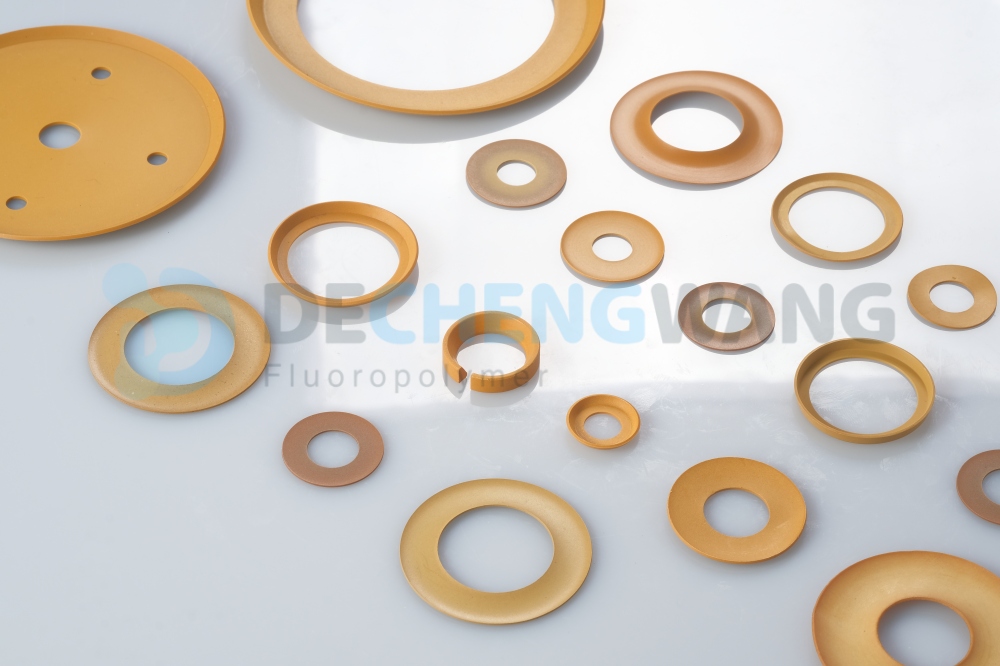
When it comes to machines and industrial appliances, there are a lot of basic, essential industrial components that are a vital part of the machinery. Seals and gaskets are good examples of such components. These are machine parts that are used to prevent leakage in different types of systems.
As for industrial applications, many often confuse seals and gaskets. There is a common misconception that both of these parts play the same roles in machinery. But this is untrue. Although these terms are used interchangeably, both industrial gaskets and seals perform distinct functions that differentiate one from the other.
Types of Essential Industrial Components
Due to their diverse applications and functions, components like industrial seals and gaskets are manufactured globally in very high numbers. Although these components serve similar purposes, they have different structures and unique applications.
- Seals
Seals are molded industrial parts that hold two parts of a machine together. The main functions of seals include preventing leakage and contamination in a system. Industrial seals are designed to stop contaminants and other undesirable substances from entering the system in which it is employed.
Seals are flat and round – usually, the inner ring is made of rubber whereas the outer ring is made of metal. Majorly used in dynamic moving parts and environments, seals are often found in active systems like engines, shafts, pumps, etc.

- Gaskets
A gasket is a component – it is a ringed composition of supple material like rubber to offer sealing between two non-moving parts to prevent leakage. It is also used among flanges, joints, and other mating surfaces for ensuring effective sealing.
Both seals and gaskets are used for industrial sealing but the difference lies in the places where they are employed – seals are used for dynamic surfaces whereas gaskets come in handy with static surfaces.
Properties of Seals and Gaskets
When it comes to seals and gaskets, many users have a lot of confusion regarding their applications. These two components have a lot of similarities, but there are differences in their properties and application too. We have listed the similarities and differences between the two industrial components here:
Similarities
Seals and gaskets have a lot of applications and functions in common between them. This is the reason why people often confuse the two components. Here are some of the similar aspects between gaskets and seals.
❖ Leakage Prevention
The first and foremost function of industrial seals and gaskets is to prevent leakage in both static and dynamic parts. For effective prevention, industrial rubber and elastomer seals need to operate with minimum friction and wear. With the help of elastic or magnetic force, a seal effectively prevents leakage between moving parts.
As for a gasket, it seals and prevents leakage between two static parts. The gasket material fills the surface irregularities on the mating surface and exerts compressive force. As elastomer gaskets have better flexibility and strength, they exhibit improved sealing properties and minimize leakage effectively.
❖ Chemical Resistance
One important characteristic of both industrial gaskets and seals made of elastomers and fluoropolymers is that they have excellent chemical resistance. Fluoropolymers like PTFE, PVDF, and PCTFE are inert to chemical fluids and components, making them a suitable option for chemical plants and oil and gas industries.
Most industrial components are prone to corrosion and experience wear and tear in such environments that involve strong chemicals. But gaskets and seals made of such materials can withstand corrosion and serve for a long time.
❖ Extreme Temperature Resistance
High-temperature seals and gaskets are applied widely in many industries including aerospace, automotive, and mechanical engineering industries. This is because components made of high-resistant materials like fluoropolymers withstand extreme temperatures and pressure without losing their properties.
For example, PTFE seals can withstand temperatures up to 260°C, making them a perfect choice for high-temperature applications.
❖ Pressure Resistance
Another similar function that both seals and gaskets serve is resistance to pressure. These parts not only prevent leakage in static and dynamic machine components, but they also function effectively in extreme situations of high temperature and pressure.
Both gaskets and seals are employed in many vital types of machinery, thus making it a requirement for these components to have good stability and rigidity. For example, PTFE seals are capable of withstanding pressure up to 500 psi.
❖ Friction Resistance
For industrial components such as gaskets and seals, the coefficient of friction has to be lower. This means that the seal or the gasket should be able to hold the two joining parts effectively. The lower the coefficient, the better the sealing. PTFE has the lowest coefficient of friction for any solid material – it ranges from 0.05 to 0.1
Differences
While these two industrial components have their similarities, they also vary in specific functions and applications. Here are some of the major differences between industrial seals and gaskets:
❖ Shape and Size
When it comes to shape and size, gaskets and seals differ from each other widely. Gaskets are usually manufactured in sheets and are custom-cut to suit the application. It is manufactured as flat sheets that are die-cut to fit particular machines and to accommodate bolts and similar parts. Generally, gaskets are bigger than seals.
As for industrial seals, they are manufactured in standard sizes and are cut in circles. O-rings and lip seals are perfect examples. It should also be noted that seals compact – flat and round is the most common form of seals.
❖ Rigidity
Since gaskets are used to join two static surfaces and are cut in custom shapes to fit the requirements of the machine components, it is usually softer and more flexible compared to an industrial seal. Gaskets can be compressed to a percentage of their own size – the compression percentage is somewhere between 35-50%
On the other hand, industrial rubber and elastomer seals are not very flexible. They retain certain levels of compression – this is because, unlike gaskets, seals operate between dynamic parts. This demands better compression and rigidity.
❖ Application Effect
As explained before, gaskets are mainly used to seal two flat, static surfaces. When it comes to flat mating surfaces, gaskets operate excellently – they prevent leakage and offer impressive industrial sealing. Gaskets are also used to dampen vibrations. The way gaskets are designed makes them a bad fit for dynamic surfaces.
Industrial seals are specifically made to suit dynamic surfaces. Systems like engine parts, pumps, and rotating shafts are the places where seals are commonly found. Seals are often used in ball bearings to reduce noise, apart from preventing leakage.
Applications of Gaskets and Seals
Due to their excellent leakage prevention and compression properties, seals and gaskets find applications in a wide range of industries. In specific, elastomer and fluoropolymer industrial gaskets and seals are used widely because they can withstand extreme temperatures and are chemically inert.
Common Application Fields
❖ Aerospace and Aviation
Fluoropolymer and fluoroplastic gaskets and seals are widely used in the aerospace and aviation industry for a wide range of services like the protection of key electrical components.
As these components are lightweight and highly durable, they are preferred over components made of other materials like usual rubber. High-temperature seals and gaskets also find applications in engine parts as these parts get heated often.
❖ Automotive Industry
Essential components used in the automotive industry need to be of lesser weight and have more wear resistance. Industrial seals and gaskets made of elastomers and fluoropolymers offer these qualities. As an additional advantage, they are also resistant to chemicals, making them a suitable choice in this industry.
These seals also offer sealing at high rotational speed – as seals are better at dynamic sealing, they make a better choice for applications like this. These seals also have high thermal stability and mechanical strength, making them the perfect choice for application in this industry.
❖ Mechanical Engineering
Mechanical engineering conjures images of high-temperature turbines and engines. In machine parts like this, it is inevitable that high-temperature situations arise and lead to the need for durable, temperature-resistant components.
Fluoropolymer and fluoroplastic gaskets and seals are perfect for these applications. Their low friction coefficients make it easy to offer high compressive sealing properties and prevent leakage while also reducing vibration and movement.
❖ Plumbing and Pipelines
Undoubtedly, seals and gaskets are found widely in plumbing systems. The need for preventing leakage and maintaining the right pressure across pipelines to ensure proper flow of fluids. Durable components made of elastomers and fluoropolymers make a right fit for such applications as they have a longer life compared to their metallic counterparts.
Industrial gaskets are also employed in plumbing systems for sealing static parts. As elastomer gaskets are resistant to high wear and tear, they are preferred for this application widely.

❖ Chemical Plants
Many chemical plants function in high temperature and pressure conditions – metal seals and gaskets are not suitable in these industries as they are neither temperature resistant nor chemically inert.
Fluoropolymers get this job covered well – components made of these materials can withstand extreme temperatures and are resistant to most chemicals and chemical solutions. From storing corrosive solutions to transporting them, industrial seals and gaskets come in handy everywhere.
Different Specific Uses
❖ Seals
As seals are specifically used between dynamic parts, they serve functions that gaskets cannot. For example, industrial sealing in components like shafts, pistons, and axles to prevent leakage and contamination. Different types of seals, like rotation seals and swivel seals perform these actions effectively.
Rotation seals, for instance, are used in gearboxes and axles. Made of high-performance materials like PTFE, these seals mainly serve the purpose of sealing lubricants and preventing leakage and stopping external fluids and contaminants from entering machine parts. These seals also reduce friction among dynamic parts, thus reducing energy waste and heat.
❖ Gaskets
Apart from preventing leakage, industrial gaskets also reduce vibration and offer rigidity. These components are mounted between flat surfaces such as joints and flange connections to improve the working of the machinery by minimizing vibration. As gaskets are flexible and can be cut into custom shapes, they find wide applications in many machines in different industries.
Gaskets also offer another important function, one that is often overlooked – they enhance mounting for the surfaces that it joins. This improves stability in machine components, thus offering better performance. Gaskets made of materials like PTFE offer better sealing and mounting properties.
Industrial Seals and Gaskets Material Consideration
There are a handful of considerations one should make before choosing the right material for making industrial gaskets or seals. Based on the industry where the component will be employed, the material from which it’ll be made should be chosen. Resistance, temperature limit, and0 durability are other factors to consider.
- Material Compatibility
Seals and gaskets are manufactured in a wide range of materials, starting from metals to rubbers to fluoropolymers.
- Temperature Limit
Many-a-times, gaskets or seals or employed in extreme temperatures, be it too hot or cold. For situations like these, it is better to choose components made of fluoropolymers as they have a large temperature range – for example, PTFE has a temperature range starting from -180℃ to 260℃. This makes it the perfect choice for making gaskets or seals that will be employed in such temperatures.
- Environmental Resistance
Environmental resistance can be also understood as resistance to UV, oxidation, weathering, sunlight, etc. Since seals and gaskets are widely used both inside machinery as well as in outside environments, they must be manufactured from environmentally resistant materials.
For example, PTFE is oxidation resistant as it is a fluoropolymer, and PVDF, a special material, is resistant to nuclear radiation. Weatherability also comes under environmental resistance, so one should also look out for materials that are resistant to wear.

- Pressure Resistance
Essential industrial components such as gaskets and seals are employed in extreme-pressure situations. So, it becomes a necessity for the material from which these components are made to be resistant to high pressure. Materials like PTFE can withstand up to 145 psi of pressure when it comes to thermal and oil applications.
As pressure increases, the seal or gasket should not yield to the force and expand or experience tear. This is why it is important to choose materials that can withstand pressure and compression.
- Wear and Abrasion Resistance
It goes without saying that industrial seals and gaskets need to be resistant to abrasion. Abrasion is understood as the wear and tear caused by machine parts when there is friction between them.
As seals (and gaskets) are the parts that join two different components of a machine, they will experience immense levels of wear. But these parts should be made of such materials that they should be wear-resistant and have a long life.
Material Options for Industrial Seals and Gaskets
Now let’s take a look at some of the most reliable materials that are suited to manufacture these components. These are fluoropolymers and fluoroplastics.
- PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is commonly known as Teflon. It is a fluorocarbon-based polymer white in color – it is one of the most common materials from which high-temperature gaskets and seals are made. Given below are a few specifications that make it a great choice for manufacturing seals:
- Temperature Range: The material has a wide working temperature range from -180℃ to 260℃.
- Inertness: PTFE is also chemically resistant. As an added advantage, it is also biologically inert.
- Resistance to Compression: The polymer is highly resistant to compression, making it one of the most suitable materials for making seals and gaskets.
- Flexibility: PTFE is flexible at low temperatures and has impressive thermal stability at high temperatures.
- PTFE Compounds
PTFE compounds refer to those materials that have a mixture of PTFE and some other material, like carbon-filled PTFE, glass-filled PTFE, etc. Generally, all these compounds have great physical strength and high-temperature resistance. When compared with virgin PTFE, these compounds also exhibit great resistance to wear and have a low coefficient of friction.
- Carbon-filled PTFE: Contains up to 35% of carbon – color is black. Improved resistance to load and electrical and thermal conductivity.
- Glass-filled PTFE: Contains up to 40% of glass fiber – color is cream white. Properties include improved wear resistance, chemical resistance, and optimal performance in an oxidizing environment.
- PEEK
Polyetheretherketone or PEEK is a fluoroplastic that is well-known for its high performance against chemicals. With its impressive chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and dimensional stability, it becomes one of the most favored materials for making seals. The color of the material is light brown or black.
- Temperature Range: Temperature range is from -70°C to 260°C.
- Inertness: Chemically resistant to common chemicals including acids, oils, solvents, and salts. It’s also biocompatible.
- Resistance to Compression: PEEK boasts high wear resistance and tensile strength.
- Other Properties: It’s a lightweight material. Considered to be the ideal replacement for stainless steel.
- PVDF
Abbreviated as polyvinylidene fluoride, PVDF is a special fluoropolymer that is resistant to nuclear radiation. PVDF also possesses great creep resistance, making it a suitable choice of material for seals that will experience more wear.

- Temperature Range: Wide temperature range: -50°C to 150°C.
- Inertness: PVDF has resistance against common chemical solvents like acids and oils.
- Resistance to Radiation: PVDF is resistant to ultraviolet and nuclear radiation. This makes the material a great choice for use in the nuclear power industry.
- Other Properties: This material has impressive dielectric properties. It also has low permeability.
- PCTFE
Polychlorotrifluoroethylene (PCTFE) is mainly used to manufacture seals because of its dimensional stability. The material remains stable under extreme temperatures and pressure, making it a suitable choice for manufacturing industrial gaskets and seals. This material also has better physical properties when compared to other fluoropolymers. It is translucent in appearance.
- Temperature Range: The working temperature of PCTFE is from -240°C to 150°C.
- Inertness: The material is resistant to all inorganic corrosive liquids.
- Mechanical Properties: Impressive creep resistance and retains dimensional stability over a wide temperature range.
- Other Properties: PCTFE exhibits a great stress-crack resistance factor. It has really low gas permeability.
- PFA
Commonly known as vinyl ether, perfluoro alkoxy is a fluoroplastic that is suitable for employment in both extremely high and low temperatures. It has impressive creep resistance and also possesses excellent crack resistance to stress. Apart from gaskets and seals, this material is also used to manufacture pipes and fittings.
- Temperature Range: The working temperature of PFA is from -200°C to 260°C.
- Inertness: PFA is chemically inert to a wide range of chemicals.
- Mechanical Properties: PFA is surprisingly stable at high processing temperatures. It has a low coefficient of friction and also a low dielectric constant.
- Other Properties: The material is capable of resisting ignition, thus avoiding the spread of flame in case of an accident.
Customized Seals and Gaskets Services Provider: DECHENGWANG
There are many global manufacturers of seals and gaskets but only a few manufacturers like Dechengwang are experts in this field. Dechengwang is an industry expert who has more than 10 years of experience in this field – we offer a wide range of machined components like bellows, O-rings, seals, bushings, etc.
- Customized Fabrication of Seals and Gaskets
If you are looking for a manufacturer who can customize industrial gaskets and seals, then Dechengwang is the perfect choice for you. We specialize in custom-designing of seals and gaskets in a wide range of materials like fluoropolymers and fluoroplastics. Apart from custom designs, we also offer standard designs for all our machined parts and semi-finished components.
- Multiple Sealing Material Choices
We offer a wide range of materials like fluoropolymers and fluoroplastics like PTFE, PEEK, PVDF, PFA, etc. These materials offer great advantages at extreme temperatures and withstand compression. If you are looking for materials that are chemically inert and biocompatible, our fluoropolymer solutions can help you.
Conclusion
Industrial seals and gaskets are essential to machine components that are found in all kinds of machines in a wide range of industries. Seals are components that are used to join two dynamic surfaces whereas gaskets are used to seal flat, static surfaces. Both of these components are mainly used to prevent leakage and minimize vibration.
If you are looking for a high-quality global manufacturer of gaskets and seals, Dechengwang is the one for you. Visit our website today and get an instant quote for your designs!



